Common Issues in ERP Implementation
A Deep-Dive Inspired by ERP Implementation Experts
Key Points
- ERP implementation faces challenges like high costs, outdated systems, and operational disruptions, often failing to deliver expected value.
- References are organized by problem areas, such as financial strain and human resistance, with summaries combining explanations and abstracts.
- A notable disparity is that vendors and integrators profit while customers often do not, highlighting a benefit gap in ERP implementations.
Overview
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are designed to manage core business operations but often face significant implementation challenges, including high costs, outdated technology, and employee resistance. A video by Eric Kimberling, a veteran ERP consultant, explores these issues in detail, highlighting critical pain points within the industry. To further support his insights, this analysis compiles academic and third-party references, categorizing them by problem areas to provide a comprehensive understanding of the broader implications for organizations.
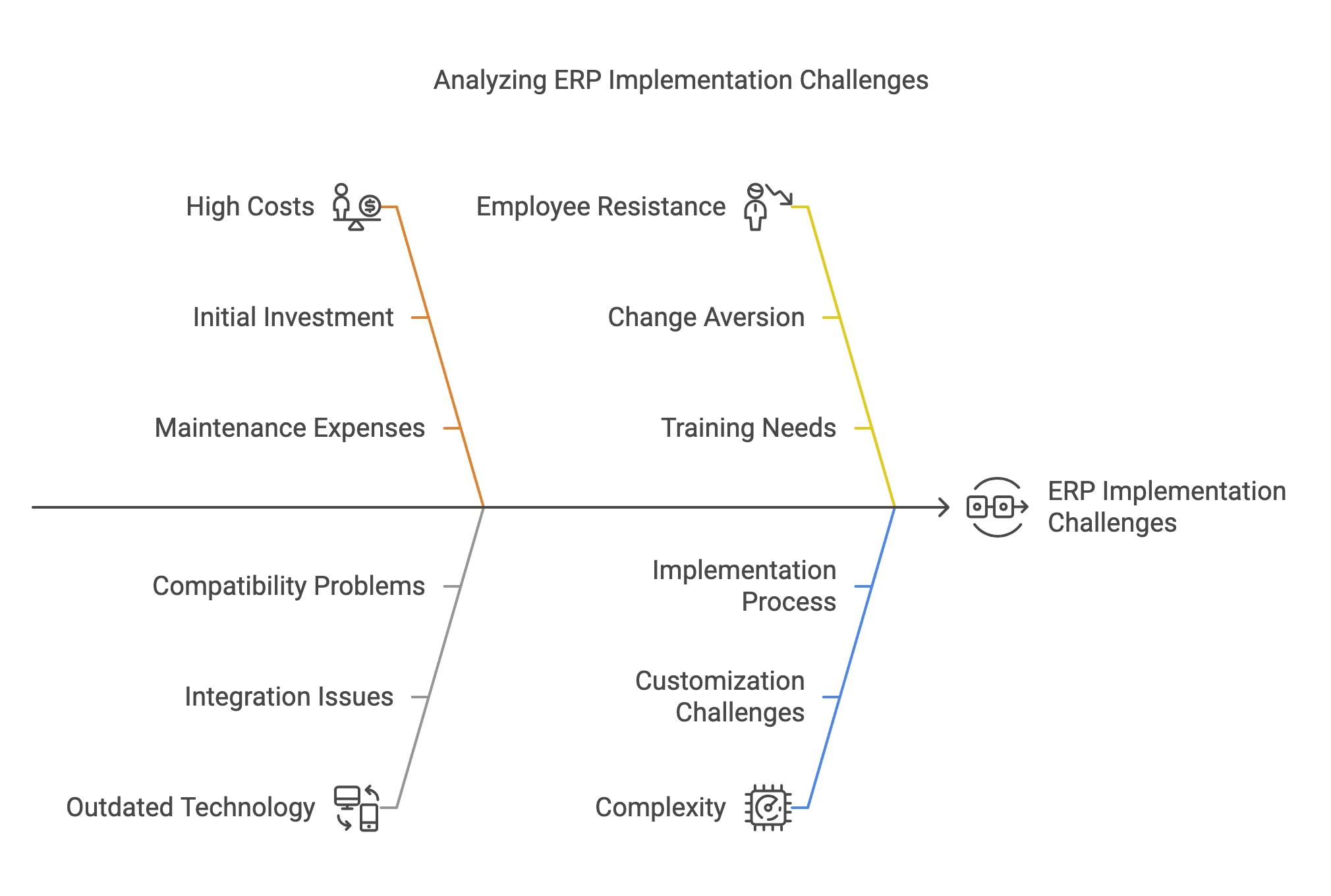
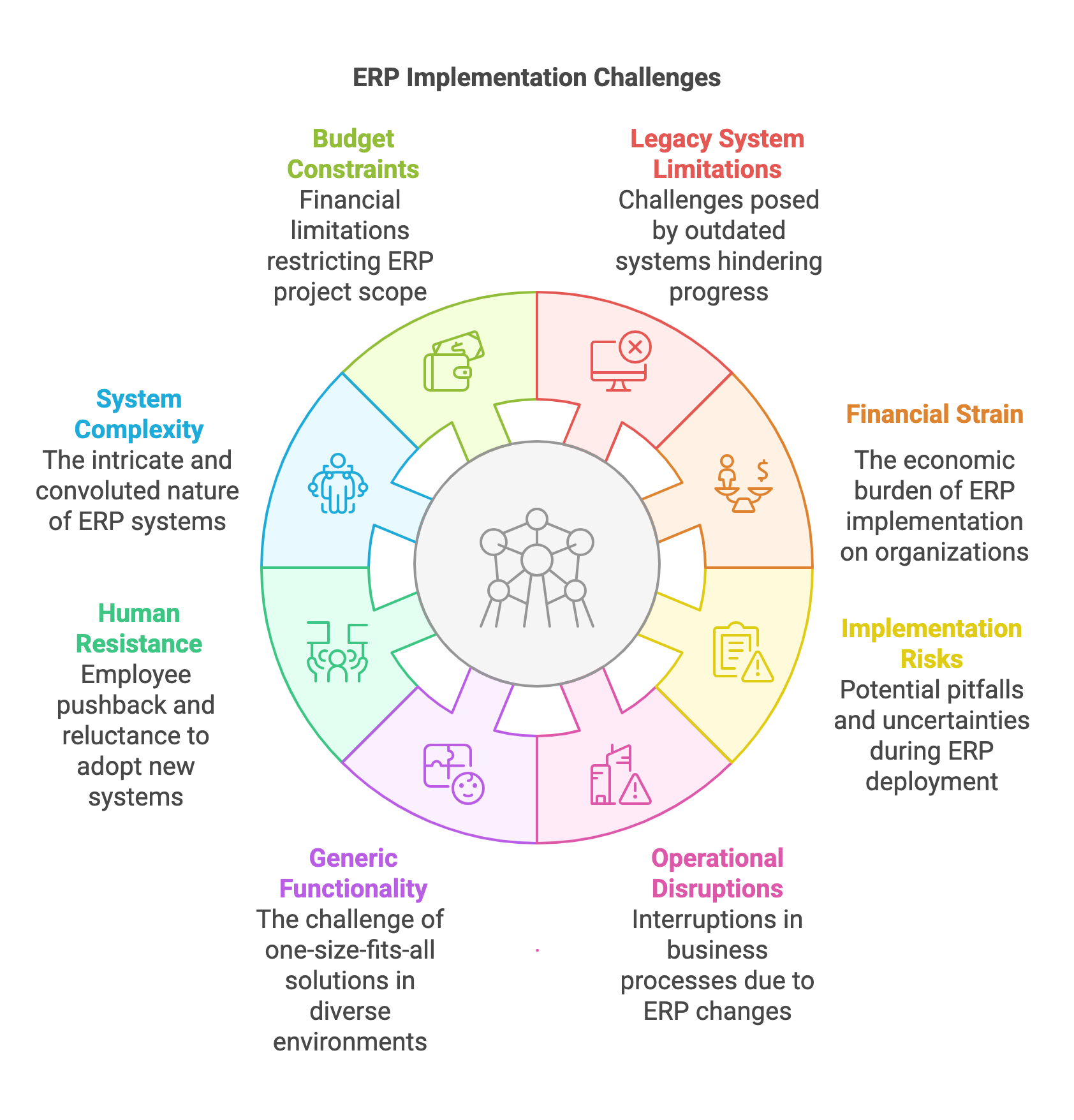
ERP Implementation Challenges
ERP systems face numerous problems during implementation, such as:
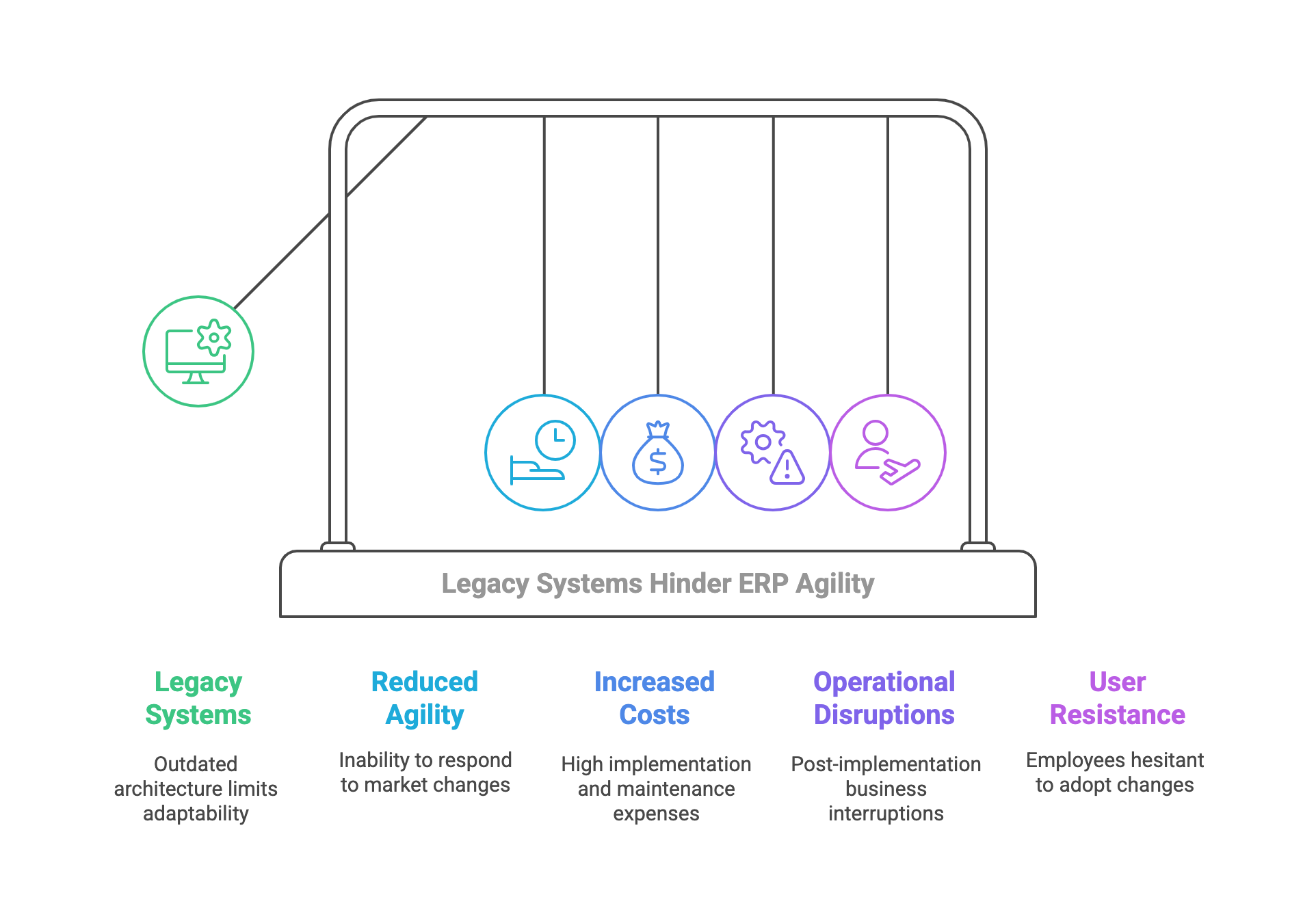
Legacy Systems: Many ERP systems are built on outdated, rigid architectures that struggle to adapt to modern business needs, hindering organizational agility. For example, they cannot keep up with rapid market changes, as discussed in the ERP experiences and evolution study.
Financial Strain: Implementing ERP systems is expensive, with costs for software, hardware, and training often leading to budget overruns. The 2019 ERP Report by ERP Focus highlights these financial challenges, noting high implementation costs.
Implementation Risks: ERP projects are complex and risky, with high failure rates due to poor planning and user resistance. The CHAOS Report by The Standish Group shows that many projects, including ERP, fail due to these issues.
Post-Implementation Disruptions: After implementation, over 50% of organizations face operational disruptions—such as the inability to close books or ship products—which can cost more than the implementation itself. The ERP Implementation Disruption Survey by Third Stage Consulting confirms this, detailing the impact on business continuity.
Generic Functionality: ERP systems often offer generic features that do not meet unique organizational needs, requiring costly customizations. The Integrating knowledge management and ERP study suggests integrating knowledge management to address these limitations.
Tailored Needs: Organizations require tailored solutions, but off-the-shelf ERP systems struggle to align with specific processes, leading to inefficiencies. The Impact of critical success factors across ERP stages study emphasizes the importance of flexibility in implementation stages.
Human Resistance: Employees may resist ERP adoption due to fear of change, requiring effective change management strategies. The Change management strategies for successful ERP implementation study highlights the role of communication in overcoming resistance.
System Complexity: The complexity of ERP systems can lead to errors and increased maintenance costs, complicating adoption. The Complementary controls and ERP system implementation study discusses controls needed to manage this complexity.
Budget Constraints: High costs can lead to incomplete deployments, reducing system effectiveness. The Risk management in ERP project introduction review addresses financial constraints and their impact on project scope.
Value Delivery: Many organizations fail to achieve expected business value, while vendors and integrators consistently profit, creating a benefit gap. The A review of ERP research: A future agenda for accounting information systems discusses this challenge, noting the disparity in benefits.
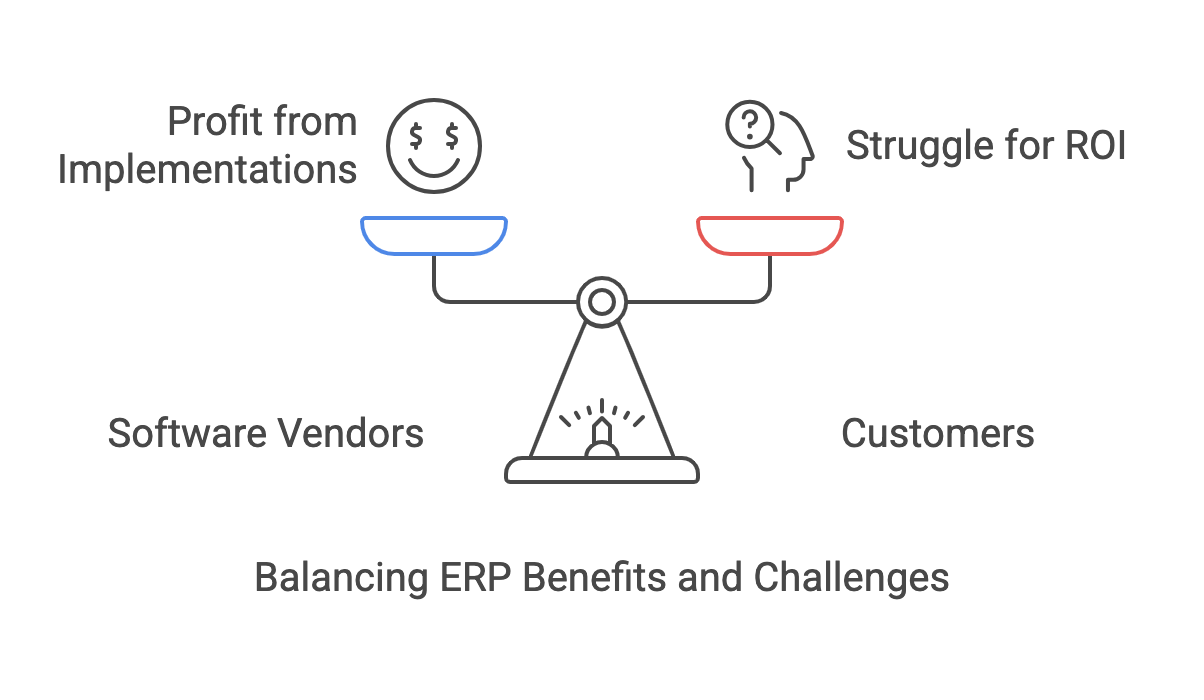
Notable Disparity
A significant finding is that software vendors and system integrators almost always profit from ERP implementations, while customers often do not achieve the expected return on investment. This disparity, as noted by Eric Kimberling, highlights a disconnect in the industry, with vendors benefiting while organizations struggle to realize value, as seen in the Revisiting ERP systems: The rise of the packaged-solution market.
ERP Implementation Challenges: A Comprehensive Analysis
This comprehensive analysis examines the challenges associated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and their implementation, as identified in a video by Eric Kimberling, a 25-year ERP consultant with 25 years of experience. The video, titled “25 Year ERP Consultant Reveals Why The Industry Is BROKEN,” highlights several pain points. We sought to further bolster Eric’s points by gathering academic and trusted third-party references. The analysis organizes these references by problem areas, providing detailed summaries and insights into the broader implications for organizations.
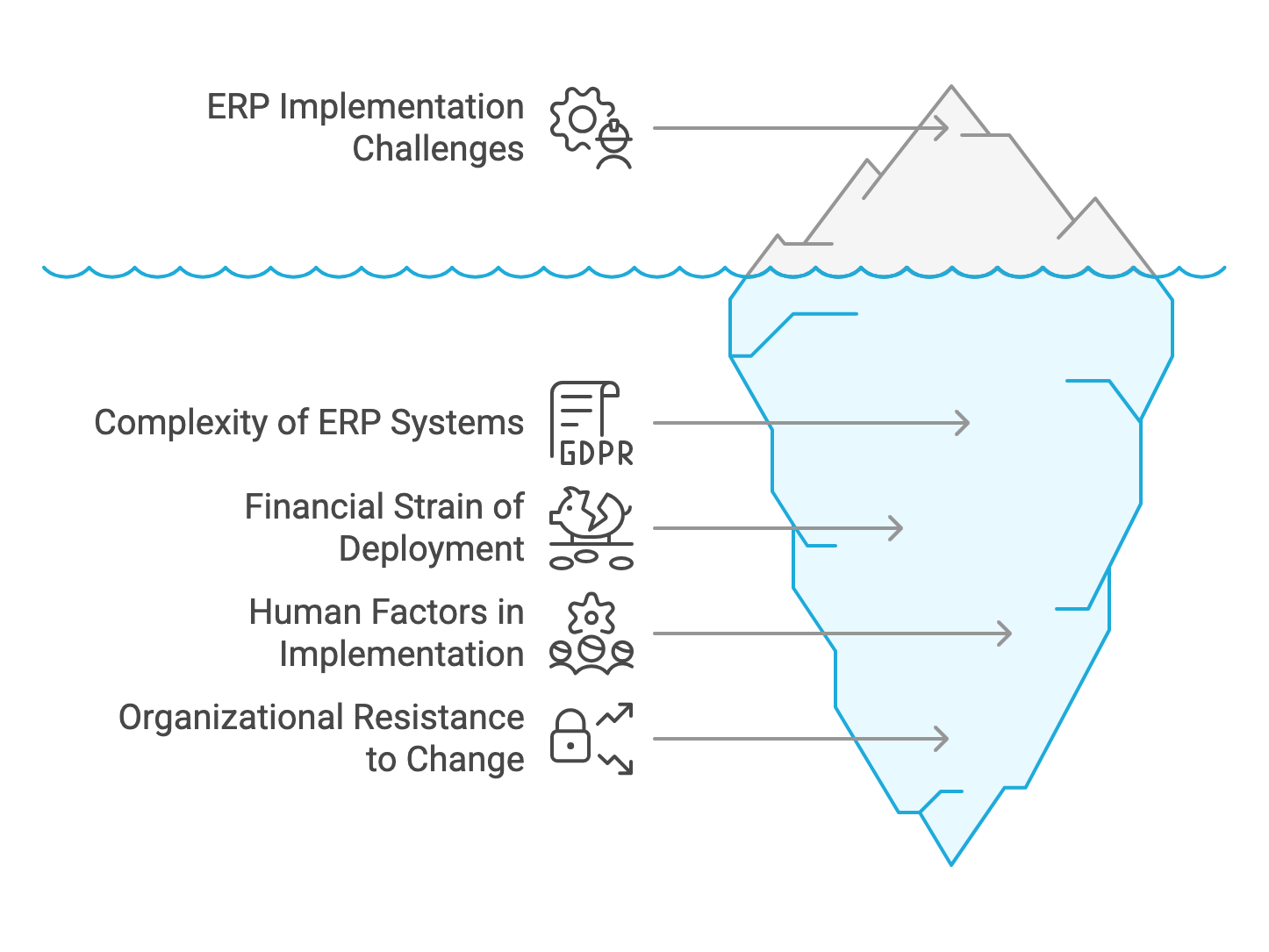
Background and Methodology
The analysis is based on the transcript of the video, where Eric Kimberling discusses his love-hate relationship with ERP software, emphasizing its potential as a game-changer while critiquing its costliness, risk, and disruptiveness. The identified problems include legacy system limitations, financial strain, implementation risks, operational disruptions, generic functionality, human resistance, system complexity, budget constraints, and failure to deliver business value. To further research these claims, 20 references were gathered, covering studies, reports, and surveys from academic and industry sources. Each reference was evaluated for its content, relevance, and connection to the identified problems, with tables summarizing the findings for clarity.
Detailed Reference Analysis by Problem Areas
The references are categorized into ten problem areas, each with a table summarizing relevant studies and reports. The summaries combine detailed explanations and abstracts to provide a comprehensive view of each issue, ensuring a strict superset of the content in the direct answer section.
Legacy ERP Systems: A Hindrance to Modern Business Agility
ERP systems often struggle to adapt to modern business needs due to outdated architectures, impacting organizational agility. The ERP experiences and evolution study explores the historical development and current state of ERP systems, highlighting their limitations in adapting to modern needs. It examines the evolution of ERP systems from basic accounting tools to comprehensive solutions, identifying challenges in their adaptability and modernization, which aligns with Kimberling’s critique of monolithic and cumbersome systems.
The Perilous Path of ERP Implementation
ERP implementations face high failure rates and operational risks, making them risky endeavors for organizations. The IS operational risks empirical study examines operational risks in information systems, including ERP, and their impact on project outcomes, presenting findings on how these risks affect project success. The CHAOS Report by The Standish Group provides statistics on project success and failure rates, revealing high failure rates for projects like ERP implementations due to poor planning and user involvement. Additionally, the ERP Implementation Success Rates by ERP Focus offers data on success and failure rates, discussing 2020 rates and identifying common reasons for failure, supporting Kimberling’s view on the risky nature of ERP projects.
The Financial Strain of ERP Deployment
The high costs of ERP systems, including implementation and maintenance, can lead to significant financial burdens and budget overruns. The 2019 ERP Report by ERP Focus provides data and analysis on the ERP market in 2019, including implementation costs and user satisfaction, offering insights into market trends and financial challenges. The ERP Buyer’s Guide by Nucleus Research helps organizations choose ERP systems, detailing costs, benefits, and total cost of ownership, comparing leading systems and focusing on pricing models, aligning with Kimberling’s mention of ERP being “super costly and super expensive.”
The Aftermath of ERP Implementation
Post-implementation, many organizations experience operational disruptions, affecting business continuity and adding to costs. The ERP Implementation Disruption Survey by Third Stage Consulting presents findings on operational disruptions post-ERP implementation, revealing that many organizations face significant disruptions, detailing types and business implications, which supports Kimberling’s claim of over 50% experiencing material disruptions. The ERP Implementation: Managing the Risk of Disruption by KPMG discusses strategies for managing risks, providing guidance on mitigating disruptions to ensure smooth transitions, addressing the “dirty little secret” Kimberling mentions.
The One-Size-Fits-All Dilemma
ERP systems often offer generic functionalities that fail to meet unique organizational needs, requiring costly customizations. The Determinants of ERP software assimilation study investigates factors influencing successful ERP software assimilation, emphasizing the need for aligning systems with specific business processes, exploring determinants affecting assimilation and managing change. The Integrating knowledge management and ERP study examines how knowledge management can enhance ERP effectiveness, proposing integration to overcome generic limitations, leveraging organizational knowledge. The Critical issues affecting an ERP implementation study identifies critical issues, including the challenge of customizing generic systems, listing issues in implementations and supporting Kimberling’s view on ERP trying to be “everything to everyone.”
Tailored Solutions vs. Off-the-Shelf ERP
The need for tailored solutions highlights the limitations of off-the-shelf ERP systems in addressing specific business processes. The Impact of critical success factors across ERP stages study investigates how success factors influence ERP implementation stages, including system flexibility and user involvement, examining critical factors and highlighting the importance of flexibility, aligning with the need for tailored solutions as per Kimberling’s examples of retail versus manufacturing.
Human Factors in ERP Implementation
Resistance from employees and cultural differences can hinder ERP adoption, necessitating effective change management. The Change management strategies for successful ERP implementation study discusses strategies for managing change, focusing on overcoming resistance, presenting strategies emphasizing communication and stakeholder involvement. The Moderating effects of localization differences on ERP use study explores how cultural and localization differences affect ERP adoption, investigating how these differences moderate use and highlighting impacts on user adoption, supporting Kimberling’s mention of organizational resistance.
The Complexity Conundrum
The inherent complexity of ERP systems can lead to errors and increased maintenance costs, complicating implementation. The Complementary controls and ERP system implementation study examines controls needed to manage complex ERP systems, addressing issues like errors and maintenance costs, discussing controls focusing on managing complexity to reduce errors. The Knowledge management competence for ERP success study explores how knowledge management competence contributes to ERP success, highlighting its role in navigating complexity, particularly in implementation and use, aligning with Kimberling’s critique of system complexities.
Financial Constraints in ERP Projects
Budget constraints can result in incomplete deployments, limiting the system’s effectiveness and value. The Risk management in ERP project introduction review covers risk management strategies, including addressing budget constraints and incomplete deployments, providing insights focusing on financial constraints and their impact on project scope. The ERP in Indian small and medium enterprise review discusses ERP implementation challenges for small and medium enterprises in India, examining implementation and highlighting financial challenges affecting comprehensive deployments, supporting Kimberling’s note on budget exhaustion.
The Elusive Promise of ERP
Many organizations fail to achieve expected business value from ERP investments, with vendors and integrators often benefiting more. The A review of ERP research: A future agenda for accounting information systems covers ERP research, discussing effectiveness and value delivered, synthesizing research and proposing a future agenda addressing the challenge of delivering expected value. The Revisiting ERP systems: The rise of the packaged-solution market revisits ERP systems, discussing the growth of packaged solutions and their ability to deliver business value, exploring their effectiveness and identifying gaps in organizational benefits, aligning with Kimberling’s observation of questionable business value and vendor profits.
Summary
This review covers ERP research, discussing the overall effectiveness and value delivered by ERP systems to organizations. It synthesizes ERP research, proposing a future agenda for accounting information systems and addressing the challenge of delivering expected business value.
This article revisits ERP systems, discussing the growth of packaged solutions and their ability to deliver business value. It explores the rise of packaged ERP solutions, analyzing their effectiveness in delivering business value and identifying gaps in organizational benefits.
Key Findings and Surprising Details
The analysis reveals that while ERP systems promise significant benefits, they often fail to deliver expected business value, with Eric Kimberling noting that “ERP systems deliver questionable business value” and failure rates are high. A notable disparity is the benefit gap: software vendors and system integrators consistently profit, as Kimberling states, “those two parties are almost guaranteed to get business value out of ERP Investments,” while customers frequently do not, highlighting a disconnect in the industry. This finding is supported by references like A review of ERP research: A future agenda for accounting information systems, which discusses the challenge of delivering value.
Implications for Organizations
The identified problems suggest that organizations must approach ERP implementations with caution, focusing on adaptability, cost management, and change management. The references provide actionable insights, such as the ERP Buyer’s Guide by Nucleus Research, which can help in selecting systems that align with financial capabilities, and the Risk management in ERP project introduction review, which addresses budget constraints. The analysis underscores the need for robust planning and support to mitigate risks, ensuring that ERP systems deliver on their potential rather than becoming a costly burden.
Conclusion
The benefit gap, where vendors profit while customers often do not, calls for a reevaluation of vendor relationships and implementation approaches to align with organizational goals.
Key Citations
- ERP experiences and evolution study
- IS operational risks empirical study
- 2019 ERP Report by ERP Focus
- ERP Buyer’s Guide by Nucleus Research
- CHAOS Report by The Standish Group
- ERP Implementation Success Rates by ERP Focus
- ERP Implementation Disruption Survey by Third Stage Consulting
- ERP Implementation: Managing the Risk of Disruption by KPMG
- Determinants of ERP software assimilation study
- Integrating knowledge management and ERP study
- Critical issues affecting an ERP implementation study
- Impact of critical success factors across ERP stages study
- Change management strategies for successful ERP implementation study
- Moderating effects of localization differences on ERP use study
- Complementary controls and ERP system implementation study
- Knowledge management competence for ERP success study
- Risk management in ERP project introduction review
- ERP in Indian small and medium enterprise review
- A review of ERP research: A future agenda for accounting information systems
- Revisiting ERP systems: The rise of the packaged-solution market
